The Tropic of Cancer, located approximately 23° north of the Equator, is one of the most important imaginary lines on Earth’s map. It marks the northernmost point where the Sun appears directly overhead at noon, which happens during the June solstice. This unique line passes through many countries, playing a significant role in shaping their climate, weather patterns, and geographical features.
In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the Tropic of Cancer. You’ll discover the countries it crosses, the meaning behind its name, and its impact on Earth’s geography. We’ll also provide a detailed map to help you visualize its path and understand how it influences the diverse environments around it.
Whether you’re a student, a geography enthusiast, or preparing for competitive exams, this complete guide to the Tropic of Cancer will deepen your understanding of the Earth-Sun relationship and the fascinating regions this line touches. Let’s dive in!
◾Also Explore All Notes on Indian Geography
Tropic of Cancer Overview
Role in Climate
- The Tropic of Cancer significantly influences climate patterns and seasonal changes in the regions it passes through.
Definition
- Known as the Northern Tropic, it is one of the five major circles of latitude on Earth.
Significance
- Marks the northernmost latitude where the Sun can appear directly overhead at noon during the June solstice.
Occurrence
- This phenomenon happens when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted at its maximum angle toward the Sun.
Current Location
- Positioned at approximately 23°26′10.0″ (23.43611°) north of the Equator.
Variability
- The latitude of the Tropic of Cancer is not fixed; it shifts slightly over time due to changes in the Earth’s axial tilt.
Impact
- Studying the Tropic of Cancer provides insights into Earth’s dynamic systems and its interaction with the Sun, shaping our planet’s diverse climates.
The Significance of the Tropic of Cancer
1. Global Climate Impact
- The Tropic of Cancer greatly influences global climate systems, shaping the diverse ecosystems and environments found within the tropical region.
2. Geographical Landmark
- Acts as a key geographical marker, dividing the Earth into the tropics (between the Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn) and the subtropics.
3. Defining the Tropics
- The region between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn is known as the tropics, marked by consistent sunshine and warm temperatures.
4. Climate Stability
- Tropical areas experience a stable climate with minimal temperature variation throughout the year, fostering unique biodiversity and ecosystems.
5. Countries Affected
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through several countries, leaving a profound impact on their climates, agricultural practices, and local ecosystems.
6. Influence on Weather and Biodiversity
- This latitude plays a crucial role in shaping weather patterns, including monsoons, dry seasons, and agricultural cycles, thereby affecting the biodiversity of regions it touches.
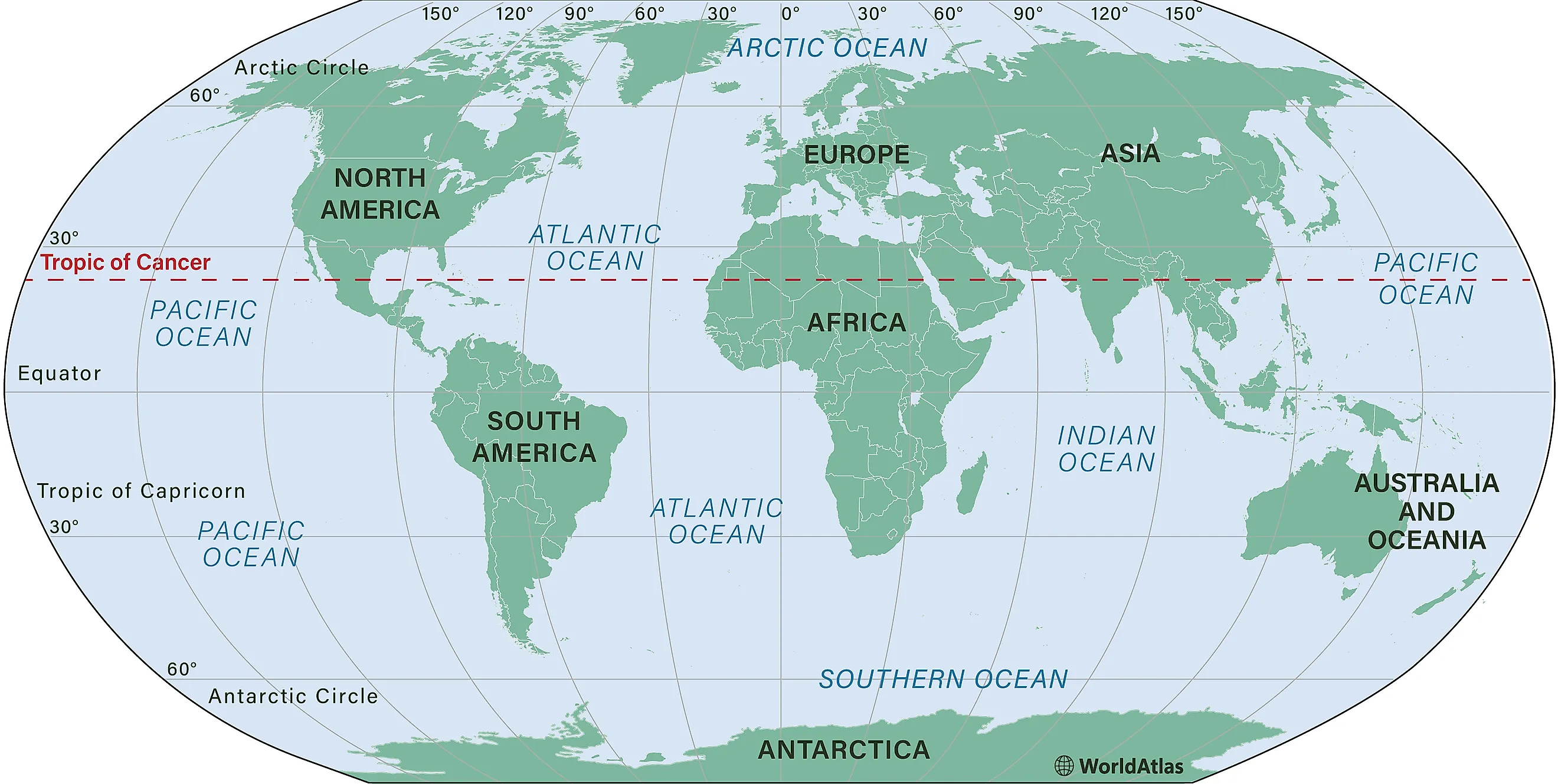
The Origin of the Name “Tropic of Cancer”
1. Connection to the Zodiac
- The name “Tropic of Cancer” originates from the zodiac sign Cancer, reflecting ancient astronomical observations.
2. Historical Alignment
- In ancient times (before the Common Era), the Sun aligned with the Cancer constellation during the June solstice.
3. Astronomical Changes
- Over time, due to the precession of the equinoxes, the Sun now aligns with the constellation Taurus during the June solstice.
4. Name Persistence
- Despite this astronomical shift, the name “Tropic of Cancer” remains in use for historical and traditional reasons.
5. Meaning of “Tropic”
- The word “tropic” comes from the Greek term “trope” (τροπή), meaning “turn” or “change”, reflecting the Sun’s apparent motion at solstices.
6. Sun’s Apparent Motion
- The Tropic of Cancer represents the northernmost point on Earth where the Sun’s rays are directly overhead before it “turns back” southward.
7. Importance in Geography
- Understanding the origin of the Tropic of Cancer connects us to the ancient practices of celestial observation, which have shaped modern geographical terminology.
The Ever-changing Position of the Tropic of Cancer
1. Earth’s Dynamic Nature
- The Tropic of Cancer reflects the fascinating dynamics of Earth’s movements and their influence on geographical lines.
2. Constant Shift
- Unlike fixed landmarks, the Tropic of Cancer’s location is not permanent and shifts over time.
3. Axial Precession
- This shift is due to axial precession, a phenomenon caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon on Earth.
4. Wobble Effect
- Earth’s axis experiences a slow wobble, affecting the Tropic of Cancer’s latitude and position over centuries.
5. Current Axial Tilt
- Earth’s axial tilt is currently 23.4 degrees, oscillating between 22.1° and 24.5° over a 41,000-year cycle.
6. Southward Movement
- As of 2000, the Tropic of Cancer is drifting southward at about 15 meters annually (0.468 arcseconds per year).
7. Historical and Future Latitude
- In 1917, its latitude was 23° 27′N, and it is projected to shift to 23° 26′N by 2045.
8. Relationship with Capricorn
- Despite its drift, the relative position of the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn remains stable, maintaining their significance as major latitude lines.
Geography of the Tropic of Cancer
1. Latitude and Environment
- The Tropic of Cancer demonstrates the link between latitude and environmental conditions, influencing weather patterns, biodiversity, and climate.
2. Global Reach
- It spans approximately 17 countries across three continents: Africa, Asia, and North America, marking a significant geographical boundary.
3. Notable Crossings
- As the Tropic moves eastward from the Prime Meridian, it passes through several important locations with unique climates and ecosystems.
4. Climate Impact
- This line plays a key role in defining climate zones, distinguishing tropical areas (south of the line) from subtropical zones (north of the line).
5. Landmark Sites
- Specific landmarks, such as Carretera 83 (Vía Corta) Zaragoza-Victoria in Mexico, showcase its precise coordinates and illustrate its gradual shift over time.
6. Subtropical and Tropical Zones
- Regions north of the Tropic of Cancer are categorized as subtropical, characterized by seasonal climates, while areas to its south belong to the tropical zone, known for consistent warmth.
7. Importance of Understanding
- Grasping the geography of the Tropic of Cancer is crucial for studying the diverse climates, ecosystems, and human settlements in its vicinity.
Climate Along the Tropic of Cancer
1. Diverse Climate Conditions
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through regions with varied climates, shaped by factors like altitude and proximity to water bodies.
2. Desert and Semi-Arid Climates
- Hot, arid conditions dominate many areas along the Tropic of Cancer.
- Sahara Desert (Africa): Characterized by extreme heat and minimal rainfall.
- Arabian Desert (Middle East): Similar to the Sahara, with intense temperatures and scarce precipitation.
3. Tropical Monsoon Climate
- Found in parts of India and Southeast Asia, this climate supports diverse ecosystems and agriculture.
- Characteristics: High temperatures and heavy seasonal rainfall are crucial for farming.
4. Temperate Climate Zones
- In regions like China and Mexico, the Tropics cross areas with temperate climates.
- Features: Clear wet and dry seasons, often supporting diverse vegetation and agriculture.
5. Biodiversity and Agriculture
- The climate variety fosters rich biodiversity and supports agricultural practices, vital for the livelihoods of millions.
6. Impact on Lifestyle and Economy
- Climatic diversity shapes the cultures, economies, and daily lives of populations along the Tropic of Cancer, influencing trade, tourism, and resource utilization.
The Role of the Tropic of Cancer in Circumnavigation
1. Global Impact on Travel
- The Tropic of Cancer plays an essential role in aviation and global travel, influencing speed records and circumnavigation standards.
2. Importance in Aviation
- The Tropic is a crucial marker for round-the-world travel, particularly in setting speed records.
3. FAI Regulations
- According to the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI), a round-the-world speed record must cover at least the distance of the Tropic of Cancer.
- Distance: Approximately 36,788 kilometers (22,859 miles).
4. Circumnavigation Rules
- To meet circumnavigation requirements, the journey must span 36,770 kilometers (22,850 miles).
- This ensures a thorough traversal of the Earth’s surface, making it a significant challenge in record-setting.
5. Key Reference Point
- The Tropic of Cancer serves as a measurable reference point for global travel records, offering a standardized distance for aviation and circumnavigation achievements.
Tropic of Cancer Overview
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | The Tropic of Cancer is one of the five significant circles of latitude on Earth. |
| Latitude | Approximately 23°26′10.0″ (23.43611°) north of the Equator. |
| Significance | Marks the northernmost point where the Sun can be directly overhead at noon during the June solstice. |
| Countries Crossed | Approximately 17 countries across three continents: Africa, Asia, and North America. |
| Climate Zones | Separates tropical (south) and subtropical (north) regions, influencing climate and ecosystems. |
| Historical Name Origin | Named after the zodiac sign Cancer, due to the Sun’s position in the constellation during the solstice. |
| Movement | Shifts southward at about 0.468 arcseconds (15 meters) per year due to axial precession. |
| Climate Characteristics | Areas experience diverse climates: arid (e.g., Sahara Desert), tropical monsoon (e.g., Indian subcontinent), and temperate (e.g., parts of China and Mexico). |
| Geographical Importance | Plays a crucial role in understanding climate, agriculture, and biodiversity in regions it crosses. |
| Circumnavigation Role | Essential for round-the-world travel records; distance covered must equal or exceed the length of the Tropic of Cancer (approximately 36,788 km or 22,859 miles). |
Explore More Indian Geography:
No post found!